Non-surgical treatment
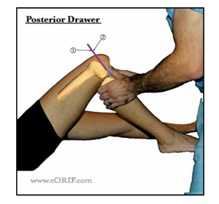
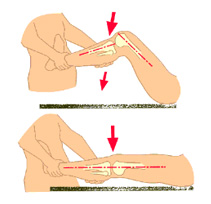
If the injury is not severe enough to merit surgically treatment, the patient may be prescribed with rehabilitation exercises, thermal (ice) treatment, compression, HILT laser, and cryotherapy to control swelling, pain, and inflammation. Alternatively, injections (PDRN, Prolo) can be used at the discretion of a specialist to promote ligament healing.
Surgical treatment
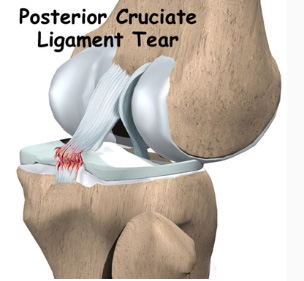
For some patients, even a moderate-grade (i.e. grade-2) injury to the PCL alone may lead to severe posterior instability. In such cases, surgical treatment must be considered as an option. As for an injury involving multiple ligament tears, the patient may start to exhibit symptoms of degeneration to the cartilage plate or the cartilage itself due to increased instability over the long-term. These types of injuries are typically treated with surgical reconstructions.
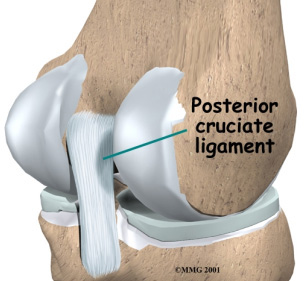
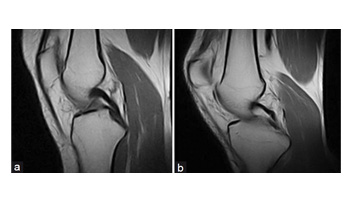
 Knee Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tear
Knee Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tear