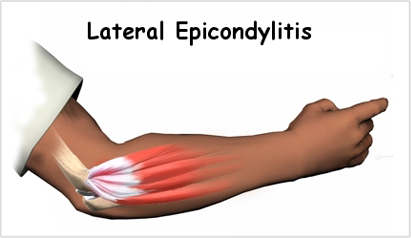
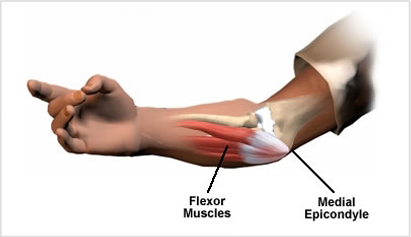
Conservative treatment
Thermal (ice) treatments and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help reduce inflammation. However, patients must refrain from repetitive pronation and supination movements or any lifting of heavy objects. If either pronation or supination is unavoidable, holding an object with the arm supinated instead of pronated may help alleviate the epicondylitis symptoms.
Surgical treatment
If patients experience symptoms for more than one year, they should consider surgical treatment of their Tennis Elbow or Golfer's Elbow. Surgical treatment options include the removal and repair of the affected area, or an arthroscope to treat the Tennis Elbow of Golfer's Elbow. Patients should consult a specialist and select the appropriate treatment depending on the condition of the affected tendon or ligament of the elbow joint.
 Elbow/Wrist Tennis & Golf Elbows
Elbow/Wrist Tennis & Golf Elbows