Conservative treatment
Patients may wear a brace to reduce weight load, which can potentially help put less strain on the injured ankle. Alternatively, patients may choose injections or Orthopedic Manipulative Physical and Thermal (Cold) Therapy.
Surgical treatment
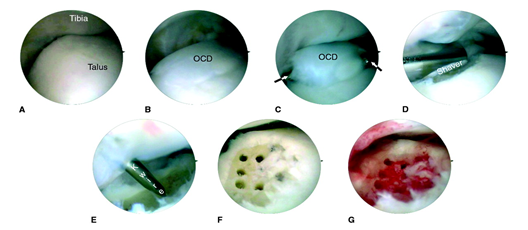
Surgical treatment depends on the condition of the articular cartilage. An arthroscope may be used to improve the stability of the injured joint, anchor loose bodies in their original positions, or remove loose bodies altogether. In this process, the specialist may elect to use a microfracture surgery technique that drills microscopic holes in the bone under the cartilage.
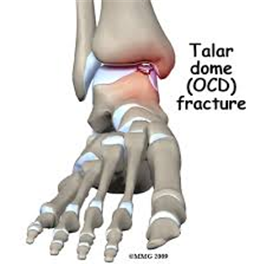
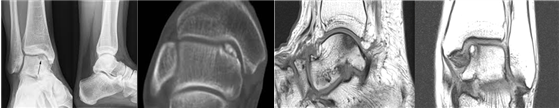
 Foot/Ankle Ankle Cartilage Injury (Osteochondritis Dissecans, OCD)
Foot/Ankle Ankle Cartilage Injury (Osteochondritis Dissecans, OCD)